



- Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Cylindrical roller bearings (CRBs) have a simple structure of cylindrical rollers in linear contact with the raceways. They offer high load capacity under primarily radial loads. Low friction between the rollers and ring ribs makes these bearings suited for high speed rotation.
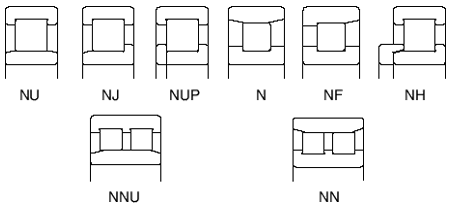
Single-row bearings are designated as NU, NJ, NUP, N, or NF, while double-row bearings are designated as NNU or NN, depending on if side ribs are used. All types allow the inner and outer rings to be separated.
Some CRBs used as free-end bearings have no ribs so that the rings can move axially relative to each other. When the inner or outer ring has ribs on both sides and the other ring has a rib on one side, these bearings can take some axial load in one direction.
Double-row cylindrical roller bearings have high radial rigidity and are used primarily for the main shafts of precision machine tools. Cages are typically made of pressed steel or machined brass, but molded polyamide resin cages are used for some models.
NSK offers a variety of CRB types to suit your needs.
Types of Cylindrical Roller Bearings
NU, N, NNU, NN: Suitable as free-end bearings.
NJ, NF: Can sustain limited axial loads in one direction.
NH, NUP: Suitable as fixed-end bearings. NH types are comprised of a NJ-type CRB with a HJ-type L-shaped thrust collar.
- Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered roller bearings are designed so that the imagined conical apices formed by the raceways of the inner and outer rings and the rollers all converge at one point on the bearing axis. The trapezoidal tapered rollers used as the rolling elements are guided by a large rib on the inner ring.
TRBs can take radial loads and axial loads in one direction. When load is applied, the axial component generated inside the bearing generally requires the use of two opposed bearings (similar to angular contact ball bearings) or double-row bearings. Spacers are used to adjust the inner and outer rings in the axial direction to achieve the proper internal clearance. Since they are separable, the inner ring (cone) assemblies and outer rings (cups) can be mounted independently.
The HR Series increases both the size and number of rollers for even higher load capacity.
Tapered roller bearings are divided by their contact angle into normal-, medium-, and steep-angle types. In addition to double-row types, four-row tapered roller bearings are also available. Pressed cages are generally used, though large bearings may utilize pin-type cages.
- Spherical Roller Bearings
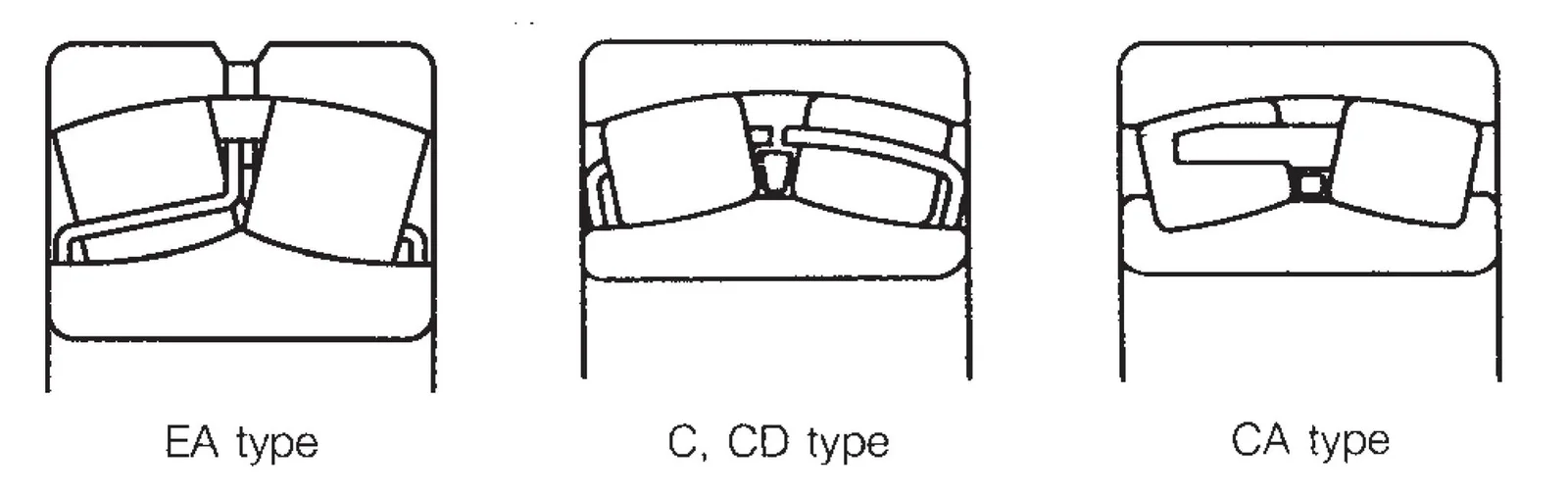
Spherical roller bearings are available in EA, C, CD, and CA types designed for high load capacity. Types EA, C, and CD have pressed steel cages, while CA uses machined brass cages. All EA types are high-performance standard NSKHPS Series bearings.
NSKHPS Series bearings have especially high load capacity, high limiting speeds, and excellent performance at temperatures up to 200°C.
Designations suffixed with E4 have an oil groove and holes on the outer ring. Since the depth of the oil groove in these bearings is limited, we recommend using an oil groove in the housing bore as well.
- Needle Roller Bearings
Needle roller bearings (sometimes called needle bearings) use long and narrow cylindrical rollers that sometimes exceed JIS/ISO size ranges. They are categorized as thrust or radial bearings based on which load direction they support. Radial types include drawn-cup and solid types, as well as application-specific track rollers (cam and roller followers). Thrust needle and thrust roller bearings respond to axial load needs.
- Home Home
- Product Product
- Information Information
- About us About us
- Form Form
- Contact us Contact us



